There are certain principles of air movement, that once understood, allow you to direct airflow to do what you want in an HVAC system. Understanding these principles can also allow you to solve comfort problems that have plagued homeowners for decades. The use of the “Coanda Effect” is one of these principles. Once understood, the way you look at duct systems and registers will change forever.
What Is The Coanda Effect?
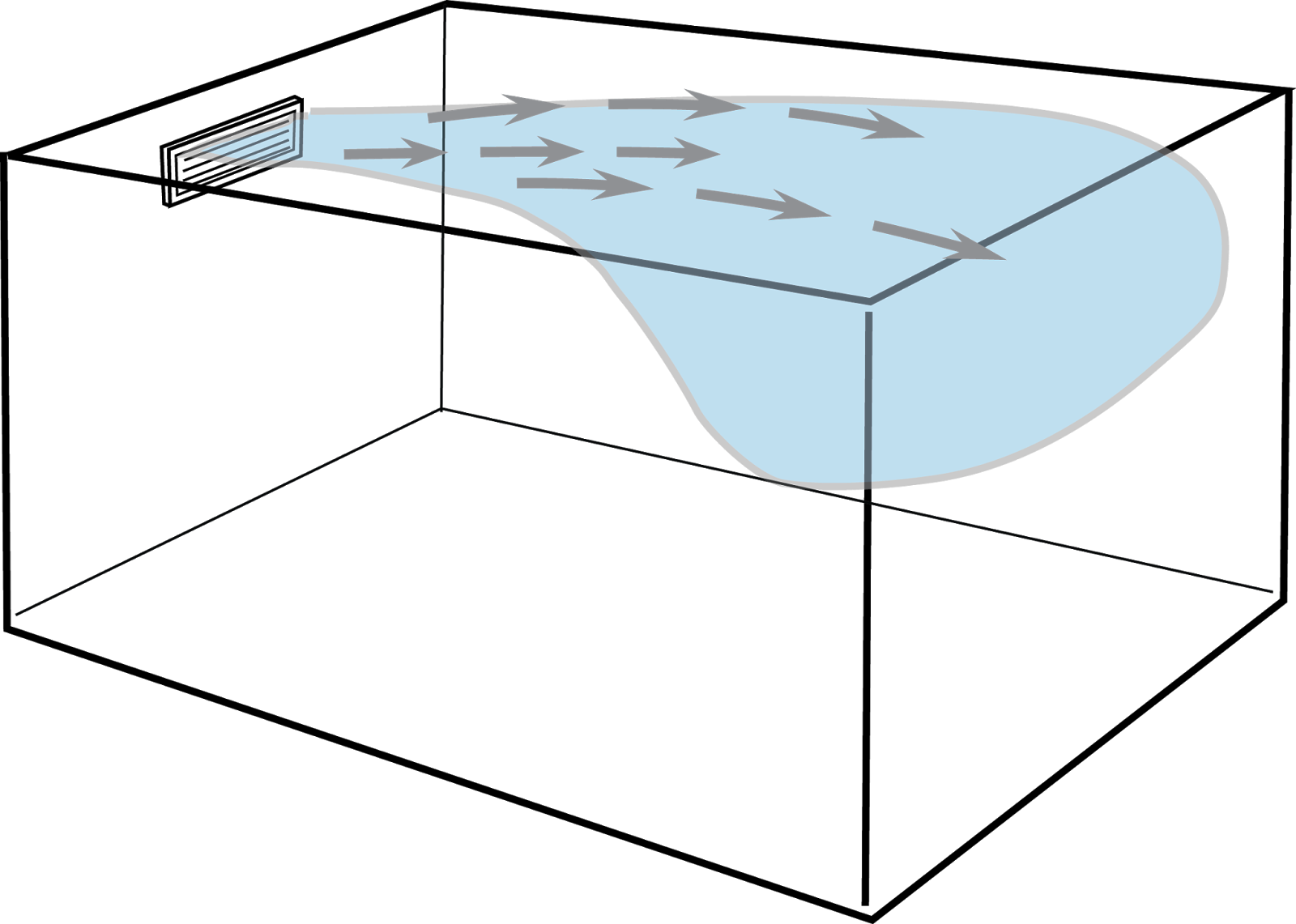
The Coanda Effect is named in honor of Henri Coanda, a Romanian aerodynamics pioneer and aircraft inventor. This phenomenon is sometimes referred to as the surface effect in many publications as well. The Coanda Effect occurs when airflow is closely projected to a parallel surface, such as a ceiling, or the walls of a duct system. When this occurs, the airflow is affected by the parallel surface it is flowing with. In simpler terms, air clings to surfaces as it moves.
The Coanda Effect creates a change in pressure, at the parallel surface, which allows the airflow to cling to the ceiling or duct wall it is flowing with. As the airflow moves along the surface, its movement is extended along that surface and projected farther into a room or down a duct than it would if it were blowing into an open space.
Any disturbances to the airflow pathway have a dramatic impact on this extended airstream being maintained. The air moving with the surface needs a smooth, obstruction free pathway to maintain the Coanda Effect. On a ceiling, items such as light fixtures, or ceiling variations, are obstructions and will interfere with the airflow being maintained. In a duct system, items such as “scoop” takeoffs, collars, and restrictive duct fittings are considered obstructions and also interfere with this action being maintained.
Changes in the direction of airflow also have an impact on the Coanda Effect. Airflow always takes the path of least resistance and wants to maintain straight line movement. If airflow has to make a sharp turn, such as turning from a trunk duct into a branch duct, the tendency of the airflow is to continue forward instead of making an immediate change in direction.
The Coanda Effect and Supply Registers
When airflow is projected into a room, from a supply register, it begins to expand almost immediately. The conditioned air flowing from the supply register also sets a large amount of room air into motion with it. This is one of the primary reasons that supply registers have more of an impact on comfort than return grilles. To truly make use of the Coanda Effect in this interaction between conditioned air and room air make sure the following conditions exist.
Understanding the Coanda Effect will cause you to think of airflow in a duct system as traffic moving down the interstate. The transitions and changes in direction have to be gradual and smooth at high rates of speed. If you suddenly block off one lane of traffic all at once, you’re going to have a problem. Airflow responds the same way inside of a duct system.
Square duct fittings contribute to this issue as they destroy airflow patterns and lead to higher pressure drops across the duct fitting. The free area of the duct fitting is displaced by the air trying to make a sharp turn. The airflow is going to take up space to make that turn due to the turbulence that has been created. Have you ever wondered why some duct fittings are longer than others when it comes to equivalent length? This is one of the contributing factors.
By using radius duct fittings in the throat and heel, the distortions in airflow patterns can be drastically reduced. The Coanda Effect can be used in your favor as the air hugs the radius fitting. The use of radius duct fittings allows for fairly uniform airflow through a turn, and reduces the pressure drops that are found with square duct fittings. You are now using the Coanda Effect in your favor as the turbulence created from the air turning is greatly reduced.
If you have ever witnessed a coil or filter that was clean in one area, while dirty in others, you have seen these uneven airflow patterns in action. No dirt typically means no airflow was moving over that section of coil or filter.
With the variety of duct fittings and registers that are available to you today, you have some choices to make. The real opportunity for you lies in being able to select duct fittings, registers, and their locations that maximize the Coanda Effect in airflow distribution.
_________________________________________________________________________
About the Author
David Richardson is a curriculum developer and instructor at the National Comfort Institiute (NCI).
This article is used with the author's permission.